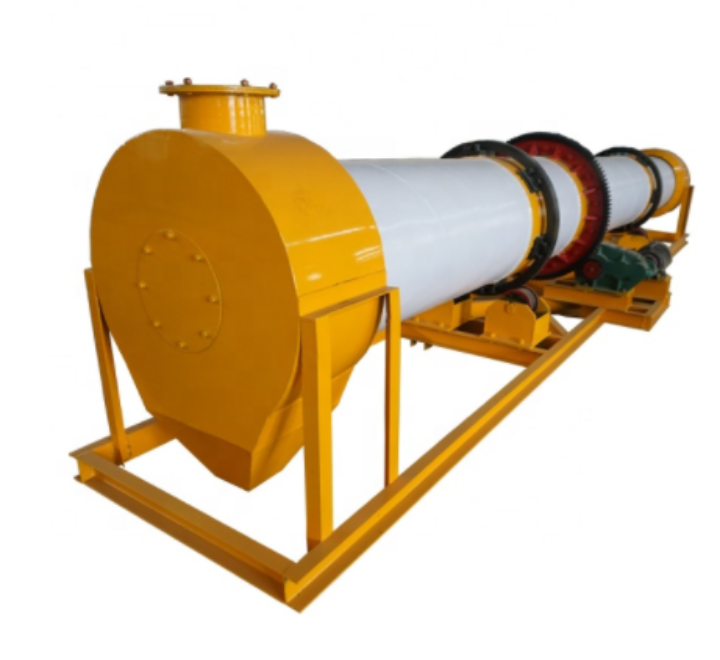

Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Direct Fired Rotary Kiln For Aluminum Hydroxide
Terbaikmachinery offers kilns utilize advanced technology to ensure efficient and precise high-temperature processing, enhancing material calcination and other thermal processes. Trust Terbaikmachinery for expertly crafted kiln solutions that deliver optimal performance and reliability.
- 0-25 mmInput Size
- Rotary kilnType
- 48-1000 TPDCapacity
Application of Rotary Kiln
Rotary Kiln Overview
Rotary kilns are essential building material equipment used in various industries. Depending on the materials processed, they are classified into cement kilns, metallurgy chemical kilns, and lime kilns. Each type serves specific purposes and is designed to meet the requirements of different industrial applications.
Types of Rotary Kilns
1. Cement Kiln
Purpose: Used for making cement clinker.
Processes: Can employ dry or wet methods.
Applications: Primarily used in cement production plants.
2. Metallurgy Chemical Kiln
Purpose: Used for various roasting and baking processes in metallurgy and chemical industries.
Applications:
Magnetic Roasting: Enhances the magnetic properties of poor iron ore.
Oxidizing Roasting: Processes chrome and nickel ores in steel factories.
Refractory Materials: Bakes high-alumina mine in refractory material factories.
Aluminum Production: Bakes chamotte and alumina in aluminum factories.
Chemical Processing: Bakes chrome ore and chrome powder in chemical plants.
3.Lime Kiln
Purpose: Used for roasting active lime and dolomite.
Applications:
Steel Works: Produces active lime for use in steel manufacturing.
Ferroalloy Plants: Processes light roasting dolomite.
Working Principle of Rotary Kilns
Structure and Components:
Rotary Cylinder: A large, cylindrical tube that rotates around its axis.
Support Rollers and Bearings: Hold and support the rotating cylinder.
Drive Gear: Powers the rotation of the kiln.
Burner: Heats the interior of the kiln to the required temperature.
Sealing Devices: Prevent heat loss and protect against external air ingress.
Operational Process:
Feeding: Raw materials are fed into the kiln from the upper end.
Heating: The burner generates heat, which raises the temperature inside the kiln.
Rotation: The cylinder rotates, ensuring uniform heat distribution and mixing of materials.
Chemical Reactions: Depending on the material and process, various chemical reactions occur as the materials move through the kiln.
Discharge: Processed materials are discharged from the lower end of the kiln.
Key Advantages of Rotary Kilns
Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of materials and industrial processes.
Efficiency: Provides uniform heat distribution and efficient processing.
Scalability: Can be used for both small-scale and large-scale production.
Automation: Modern kilns can be equipped with automated control systems for precise operation.
Environmental Control: Advanced kilns have systems to minimize emissions and environmental impact.

Rotary kilns are vital equipment in various industrial applications, ranging from cement production to metallurgy and chemical processing. Their ability to handle different materials and processes makes them indispensable in many manufacturing sectors. Understanding the specific needs of the material and the intended application is crucial for selecting and operating a rotary kiln effectively.
Advantages of Rotary Kiln
New Advancements in Rotary Kiln Technology
Rotary kilns have evolved significantly with advancements in technology. These innovations enhance energy efficiency, operational stability, and precision in fabrication and installation. Below are the key advancements in rotary kiln technology:
1. Advanced Main Driving System
New Technology Adoption: The main driving system of modern rotary kilns uses advanced technology compared to traditional magnetic and DC speed regulation systems.
Advantages:
Energy Saving: More efficient power usage reduces operational costs.
Environmental Benefits: Lower energy consumption leads to a reduced carbon footprint.
Wide Speed Adjusting Range: Offers greater flexibility in operation.
High Performance and Stability: Ensures reliable and consistent kiln operation.
2. Enhanced Fabrication and Installation Precision
Stress Relief in Supporting Devices: After welding the bases for supporting and catching rollers, a vibration aging treatment is applied. This process removes welding stress, ensuring structural stability.
Integration Fabrication: Utilizing vertical lathes and boring-milling machines for integrated fabrication ensures high precision.
Improved Installation Accuracy: These processes enhance the dimensional and locational tolerances, resulting in better installation accuracy for the rotary kiln.
3. Automation and Monitoring
Temperature Measurement: A temperature measuring point is reserved at the bearing base of the supporting roller.
Purpose: Allows for the insertion of measuring devices to automate the detection of kiln operation status.
Benefit: Provides real-time monitoring and data collection, facilitating predictive maintenance and improving operational efficiency.

These advancements in rotary kiln technology highlight the shift towards more efficient, precise, and automated systems. The adoption of energy-saving driving systems, improved fabrication techniques, and enhanced monitoring capabilities all contribute to the increased performance and reliability of modern rotary kilns. These improvements not only optimize the operational aspects but also support environmental sustainability and cost-effectiveness in industrial applications.
-
High Quality
Convenient transportation, crawler walking, no damage to the road, equipped with multi-functional accessories, Drived by oil and electricity.
-
Customized Design
The whole crushing plant adopts all-wheel drive to realize rotating direction in place, with perfect protection function, especially suitable for narrow and complex site.
-
Good Performance
The crawler crushing plant could be optional for jaw crusher, impatct crusher, cone crusher, VSI crusher etc.
Working principle
The rotary kiln from China professional manufacturer Henan Terbaik Machinery is designed for efficient processing and transformation of various materials. Here's a detailed overview of its working principle :
Structure and Operation
Cylindrical Vessel
Design: The kiln is a cylindrical vessel slightly inclined to the horizontal axis.
Rotation: It rotates slowly around its axis, facilitating the gradual movement of the material from the upper to the lower end.
Material Processing
Feeding: Materials are fed into the upper end of the cylinder.
Movement: As the kiln rotates, materials gradually move downwards, undergoing stirring and mixing.
Hot Gases: Hot gases pass along the kiln, either in the same direction (co-current) or, more commonly, in the opposite direction (counter-current).
Heat Source
External Furnace: Hot gases can be generated in an external furnace.
Internal Flame: Alternatively, a flame can be generated inside the kiln using a burner-pipe (or 'firing pipe').
Fuel Types: The fuel used can be gas, oil, or pulverized coal.
Key Features
Efficiency
Material Processing: The inclination and rotation ensure thorough mixing and gradual movement of materials, optimizing processing efficiency.
Heat Management
Counter-Current Flow: Usually, the hot gases flow in the opposite direction to the material, maximizing heat transfer efficiency.
Fuel Flexibility: The ability to use different fuel types (gas, oil, coal) provides flexibility and efficiency in heating.
Robust Construction
Durability: Designed for heavy-duty operations, the kiln is constructed to withstand high temperatures and continuous operation.

Conclusion
The rotary kiln from Henan Terbaik Machinery exemplifies advanced engineering and design for effective material processing. With its robust construction, efficient heat management, and flexible fuel options, it is well-suited for a variety of industrial applications. Enhanced by modern driving systems, precision fabrication, and automated monitoring, this rotary kiln offers reliability, efficiency, and high performance.
Specification
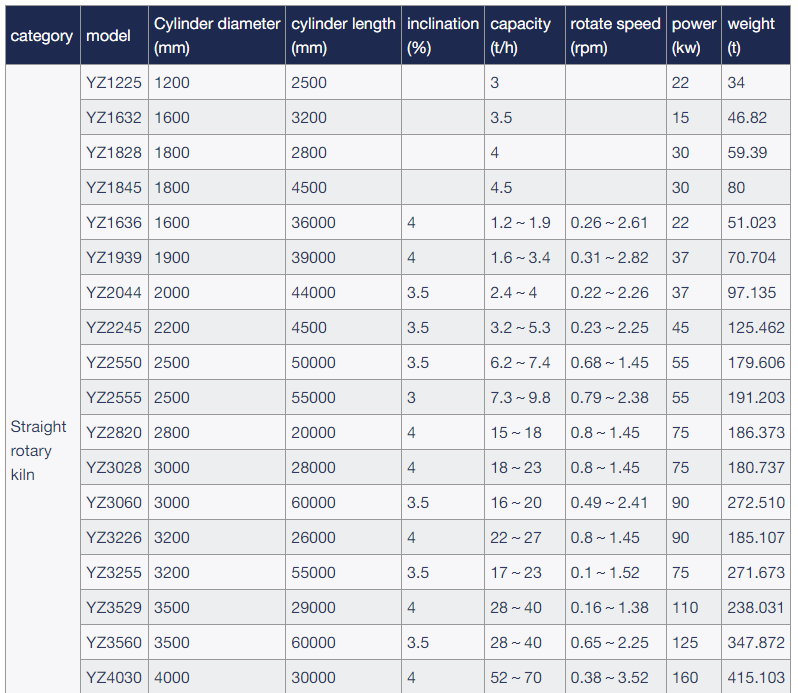
*The output will vary according to different materials, feed particle size and other factors




-
Whatsapp
 +86-19139706301
+86-19139706301
-
Wechat
 +86-19139706301
+86-19139706301
-
EmailKevin@terbaikmachinery.com
- Back


